Insurance Analytics
How to Build a Spatial Data Catalog
Contents
The Problem of Too Much
Let’s start off with a hypothetical example. Say you are the manager of an Amazon warehouse and you receive an order to ship a book (maybe The Salt Path by Raynor Winn). But none of the million things that are available in your warehouse are cataloged or labeled. As such, you find yourself scampering through each and every one of the million items that are present in your warehouse until you finally find the book that you were looking for. Hurray! You barely made it before the deadline and you give yourself a pat on the back for a job well done. Just then, the next order comes and you have to go through this hell all over again. Does this sound fun? And more importantly, does this sound like an effective way of doing business? While this may have been a hypothetical example, the digital version of this is still an unfortunate reality for many data managers.
Geospatial data is being generated at a staggering rate as a result of the increasing number of remote sensing gadgets, IoT devices and geotagging/location data available today. This should not come as a surprise seeing that all businesses, at their core, focus on people, places and assets. This makes spatial data indispensable. While capturing this data is an amazing achievement in and of itself (think about the effort that goes into getting observation instruments into space or getting a live feed from assets outfitted with sensors), the sheer volume and non-conforming formats make it very hard to manage and use it in applications.
Why is that? Well, consider the above example and replace the physical book with a spatial data layer of file. Spatial data warehouses are usually very poorly unified in terms of metadata, indexing and formatting. As such, data scientists, analysts or other end users of spatial data need to go on a hunt to find the data they are looking for, sifting through TBs worth of spatial data to find the proverbial needle in the haystack. It's safe to say that prior to being a data scientist, an actuary or an underwriter, the person looking to leverage some spatial data first needs to take up the role of a data cleaner and data manager (which is not what they are paid to do).
So, what good is having heaps of data if it’s not queryable and easy to use? Has it ever crossed your mind that having less data to begin with would have been a better bet? Be rest assured, that is not a solution. That’s a compromise. Industry leaders and trendsetters do not make compromises. They use these as an opportunity to set themselves apart from their competitors.
What’s the solution to this mismanaged data warehouse debacle? Coming up in the next section!
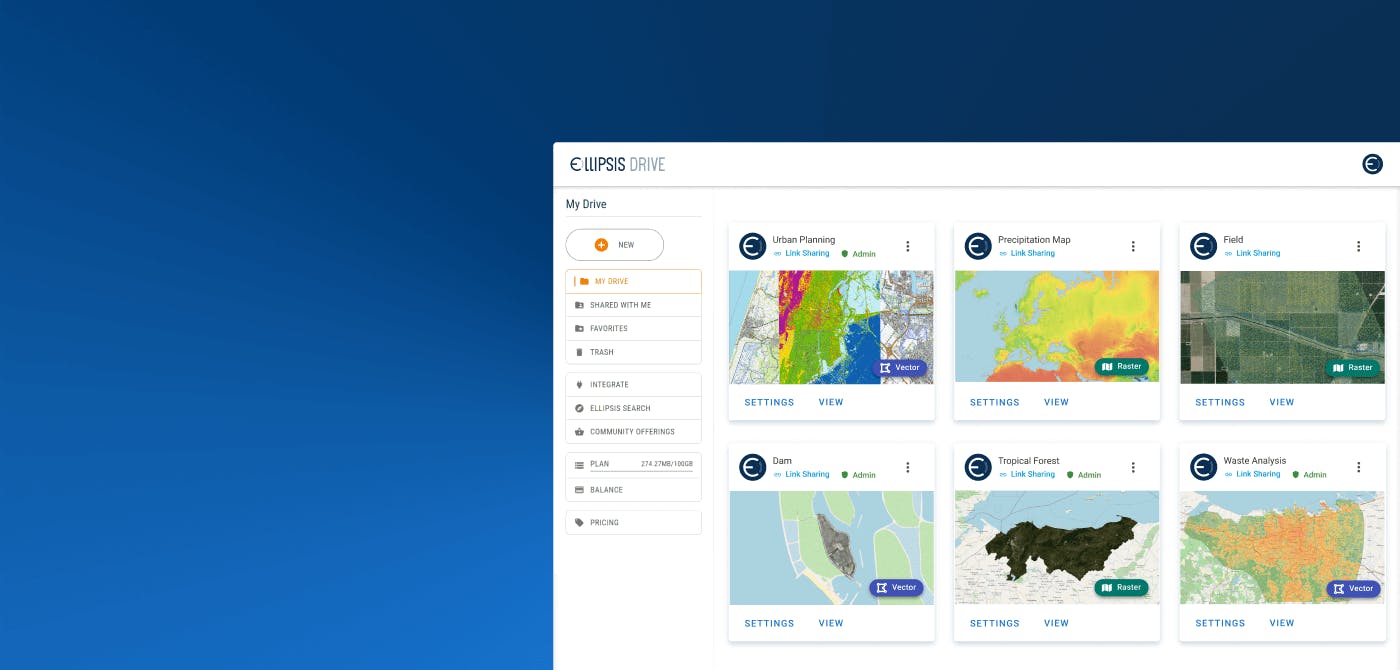
Building a Spatial Data Catalog with Ellipsis Drive
The solution is simple enough. Just like cataloging and labelling items in your Amazon warehouse the same cataloging needs to be done for your spatial data. Smart indexing makes your content findable and queryable.
Creating a spatial data catalog is easier said than done though. Unless, when you use Ellipsis Drive for this tedious task! So let ‘s take a look at how you can make your content available in a scalable, dynamic and high performance catalog that gives you easy access to all your data layers. Making your spatial content easy to search, manage, integrate and visualize in downstream processes:
Step 1: Upload spatial data files onto a familiar looking cloud-based file management system with a simple drag-and-drop feature
Step 2: Activating your spatial data to get them parsed, tiled, reprojected and indexed into a web based data layer which is ready for high performance use by any audience of your choice. This step is completely automatic!
Step 3: Visualize and manage your interactive data layers directly in a browser or integrate them into your tools, applications and workflows of choice by utilizing a wide range of packages and plugins.
Upon uploading geospatial data onto Ellipsis Drive, our backend is automatically able to detect the following metadata from the uploaded files -
- Bounds
- Resolution
- Number of bands
- Band names
- Data types
- Compression
- Properties
- EPSG Data
A few additional metadata specifications needed to be added manually such as layer name, timestamp, description and tags.
As a result of the above, your geospatial data gets indexed and becomes queryable based on the below parameters -
- Layer name
- Owner
- Tags
- Date Range
- Bounds
- Spatial extent
- Properties
- Style names
- Resolution
- Access Level
- Root
You can learn more about the technicalities of metadata upload here.
Advantages of a Spatial Data Catalog
Congratulations! Your Spatial Data Catalog is ready. Your data analysts and scientists can breathe easy once again. Let’s talk a bit about what you are about to achieve as a result of dealing with this (approximately $ 2-3M) complexity.
- 70% faster project completion for data scientists: By automation data preparation and wrapping the API with Python and R packages, your data science team can focus on analysis right away
- Migration free and compliant data management: An AWS deployment of Ellipsis Drive, allows you to run the solution in your own secure environment
- 15X faster onboarding for data vendors and partners: Cutting one month of technical implementation time for ingesting spatial data back to just 2 days.
Final Thoughts
At Ellipsis Drive, we take great pride in saying that we are the world’s first interoperable drive for geospatial data. The best solutions are the simplest ones. The ED product team has worked long and hard to build a solution that provides you with the best geospatial data management experience possible.
Start building your spatial data catalog today and get ahead of the curve. Book a free demo with our Head of Sales for a detailed walkthrough on how Ellipsis Drive can fit your business needs. We are here to help!
Liked what you read?

Subscribe to our monthly newsletter to receive the latest blogs, news and updates.
Take the Ellipsis Drive tour
in less than 2 minutes'
- A step-by-step guide on how to activate your geospatial data
- Become familiar with our user-friendly interface & design
- View your data integration options

Related Articles
Tackling Land Subsidence with Ellipsis Map Engine
Pipeline infrastructure is central to the Oil & Gas industry, enabling the safe and efficient transport of resources across long distances. But this infrastructure faces constant threats from natural
5 min read
Opportunities for the Insurance Industry (2023)
What is the difference between a challenge and an opportunity? It could be argued that they are one and the same. That a challenge is just an opportunity in disguise. In need of someone to innovate a
7 min read
Automating the Ingestion of Spatial Risk Data into Data Warehouses
In today’s data driven world, insurance companies are always seeking out new ways to enhance their decision making process and gain a competitive advantage. With the increased rate of natural catastr
5 min read