Disaster Management
Role of GIS in Disaster Management

Contents
What is the role of GIS in Disaster Management?
The need for disaster preparation is an ever-growing force worldwide. After all, history has proven that natural calamities strike arbitrarily.
Thanks to improvements in modern technology and the availability of reliable and effective solutions, facing these hurdles and obstacles has become less challenging than ever. For those that rely on geospatial measures to stay on top of possible threats and prevent greater disaster risks, many options can be very impactful.
And the most critical and impactful option of all? Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology—especially when you consider how instrumental it is in any emergency management strategy. GIS play a crucial role in disaster management by providing valuable tools and technologies for collecting, analysing, and visualizing geospatial data. Here are some key roles of GIS in disaster management:
- Risk Assessment and Planning: GIS can be used to assess and map areas prone to various hazards, such as floods, earthquakes, wildfires, or hurricanes. By integrating data on population density, infrastructure, topography, and historical event patterns, GIS helps in identifying high-risk zones, assessing vulnerabilities, and developing effective disaster management plans.
- Emergency Response and Situational Awareness: During a disaster, GIS enables emergency response teams to quickly gather and analyze real-time data from various sources, including satellite imagery, weather data, social media feeds, and sensor networks. This information helps in creating situation maps, identifying affected areas, estimating population density, locating evacuation routes, and coordinating response efforts.
- Damage Assessment and Recovery: GIS aids in post-disaster damage assessment by overlaying pre-disaster data with aerial or satellite imagery to identify and quantify the extent of damage. This information assists in prioritizing recovery efforts, allocating resources, and estimating financial losses. GIS can also facilitate the monitoring of reconstruction projects and track the progress of recovery activities.
What are the applications of GIS and Remote Sensing in Disaster & Emergency Management?
Together with the quickly evolving use of the internet, GIS technology and remote sensing has proven to be a valuable asset for those looking to stay prepared through the means of critical data.
In the past decade alone, they have been crucial in reducing disaster risks while improving planning efforts well enough to become effective at any point in time. The spatial data management solution offered by companies such as Ellipsis Drive are developed with the intention of enabling the use of GIS to understand and communicate the complexities of natural disasters.
On the surface, they are both invaluable for any emergency management effort because of its ability to predict where a natural disaster is most likely to occur. With the use of past data and geographical concepts and principles, this solution bears the potential for communities to manage risks effectively. But how does it aid in emergency management?
- Situational Awareness: Remote sensing, which involves the use of satellite imagery and aerial photography, provides up-to-date and high-resolution visual data of the affected areas. By integrating this data with GIS, emergency response teams can quickly assess the extent of the disaster, identify impacted areas, and monitor the progression of the event. This situational awareness helps in making informed decisions and allocating resources effectively.
- Damage Assessment: GIS and remote sensing assist in rapid damage assessment after a natural disaster. By comparing pre-disaster and post-disaster satellite images or aerial photographs, emergency response teams can identify areas of destruction, assess the severity of damage to infrastructure (buildings, roads, bridges), and prioritize rescue and recovery efforts accordingly. This information aids in resource allocation and planning for reconstruction.
- Hazard Mapping and Prediction: GIS and remote sensing technologies contribute to hazard mapping and prediction. By analyzing historical data, topography, and other relevant factors, GIS can help identify areas at high risk of natural disasters, such as flood-prone zones or landslide-prone areas. Remote sensing data, including weather patterns and satellite imagery, is crucial for predicting and tracking the progression of natural events, such as hurricanes, storms, or floods. This information assists emergency response teams in issuing timely warnings and implementing evacuation plans.
- Evacuation Planning and Route Optimization: GIS plays a vital role in evacuation planning and route optimization. By considering factors like population density, road network, topography, and predicted disaster impact areas, GIS can help identify evacuation routes, determine capacity of evacuation centers, and estimate transportation requirements. It assists emergency response teams in efficiently evacuating people from high-risk areas, ensuring their safety.
- Resource Management: GIS facilitates efficient resource management during emergency response. By integrating data on available resources (e.g., medical facilities, emergency supplies, temporary shelters) and overlaying it with geospatial information, emergency response teams can quickly identify the nearest resources to affected areas and allocate them accordingly. GIS helps in coordinating logistics, optimizing resource distribution, and minimizing response time.
- Communication and Coordination: GIS-based platforms and tools provide effective communication and coordination among emergency response teams. They enable real-time sharing of geospatial information, such as situation maps, evacuation plans, and resource locations. GIS allows different response teams and agencies to collaborate, exchange data, and make informed decisions based on a common operational picture.
Conclusion
By combining GIS and remote sensing technologies, emergency response teams can enhance their capabilities in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. These tools enable faster decision-making, improved resource allocation, and more effective coordination, ultimately saving lives and minimizing the impact of natural disasters.
Ellipsis Drive offers mapping as a service, geospatial insights, and geospatial data analysis. If you're looking to improve your emergency management efforts, get in touch with us today!
Liked what you read?

Subscribe to our monthly newsletter to receive the latest blogs, news and updates.
Take the Ellipsis Drive tour
in less than 2 minutes'
- A step-by-step guide on how to activate your geospatial data
- Become familiar with our user-friendly interface & design
- View your data integration options

Related Articles
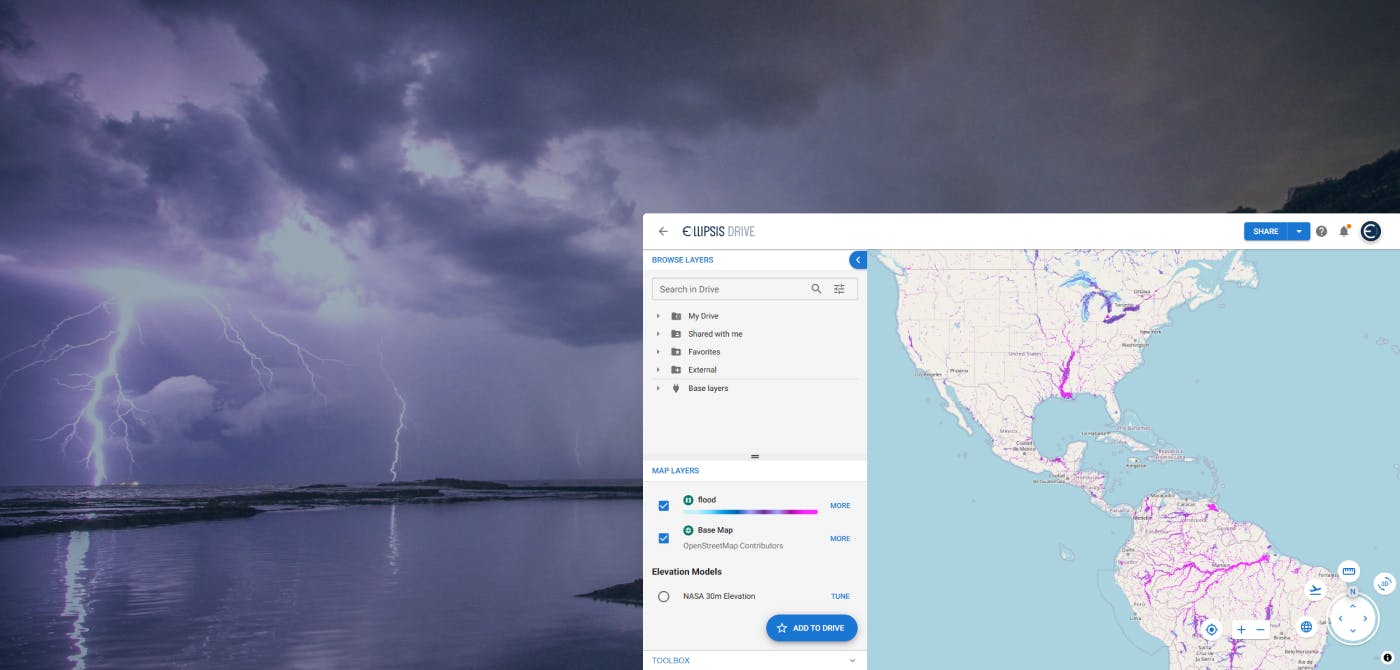
Flood Risk Management with Ellipsis Map Engine
Flooding is the most common and costliest natural disaster worldwide. In 2023 alone, global insured losses from natural catastrophes topped $123 billion, with floods accounting for a growing share of
5 min read
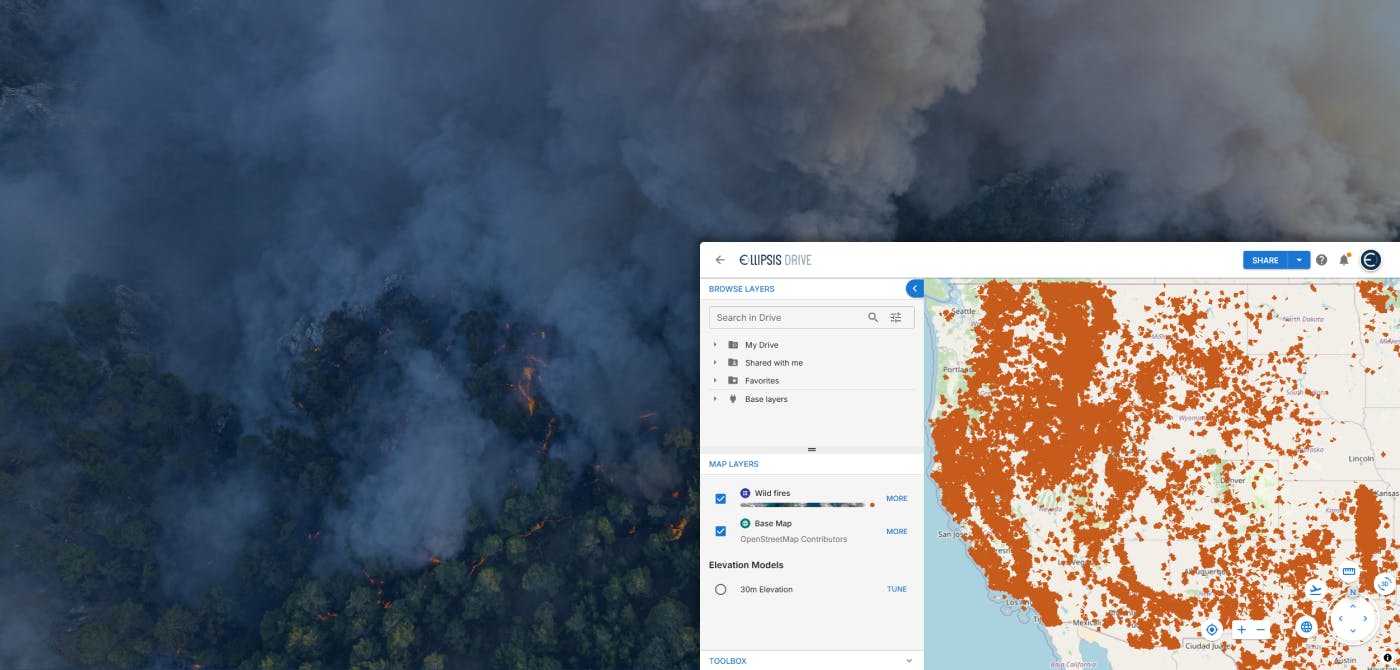
Near Real-Time Natural Catastrophe Assessment
Natural catastrophes such as earthquakes, floods, and forest fires are becoming more frequent and less predictable, largely due to the accelerating effects of climate change. This escalating volatili
6 min read
Satellite Radar Data to Monitor Land Subsidence
The Earth continues to go through drastic changes in the 21st century. As the human population rises and the exploitation of natural resources rises along with it, the Earth continues to retaliate in
3 min read